Theme: Determination of various approaches in the field of ophthalmology and Eye care
Global Opthalmology 2022
About Conference
The 9th Global Ophthalmology meeting brings together a global and interdisciplinary combination of pharmaceutical, biotech, and analytic organizations, driving colleges and clinical research institutes that make the community a great platform for sharing engagement, enhancing participatory efforts across the field and the world of experts. , and monitor developments around the world.
9th Global ophthalmology meeting provides an opportunity to connect and benefit from your fellow nationals repeatedly around the world who had Retina and Retinal Issue, Cornea, Outer Eye Disease, Neuro-Ophthalmology, Glaucoma: Visual Field Misfortune, Visual Microbiology, and Immunology, Novel to deal with Ophthalmology, Therapeutics and more.
OBJECTIVES
Our aim is to provide cataract surgeons, refractive surgeons, optometrists , opticians, young researchers, students, industrial delegates and anyone professionally involved in study of cataract and refractive surgery with an opportunity to learn about the severity of the disease, discuss interventions, look for new and advanced methods to remove cataracts and their effectiveness in treating various recovery and cataract extraction errors, and understanding local facts and barriers to effective cognitive care.
Session/Tracks
Ophthalmology is a medical department responsible for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of eye diseases and the visual system. It is a specialized medical field focused on eye health. It includes dementia, allergies and eye diseases. Historically, the science of ophthalmology has incorporated all aspects of visual function, health and illness The eye, its surrounding structures, and the visual system can be affected by many clinical conditions. Ophthalmology includes the diagnosis and treatment of such conditions, as well as microsurgery.
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage optic nerves, whose health is important for good eyesight. This damage is usually caused by unusually high pressure on your eye. Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of blindness in people over 60 years of age. It can happen at any time but is most common in adults.
Cornea Disorders and Treatments
The eye is made up of delicate and fine tissues and every part of the eye does its job of maintaining its normal vision. The cornea is the limpid part of the eye that covers the front of the eye. It covers the pupil (the slit in the middle of the eye), the iris (the coloured part of the eye), and the inner chamber (the inside filled with eye fluid). The main function of the cornea is to extract, or bend, the light.
The term “corneal disease” encompasses a variety of conditions affecting the cornea, a clear outer layer. The cornea usually repairs itself after an injury or illness, but more serious conditions - infections, degenerative diseases, degradation - needs treatment.
If you have advanced corneal disease, you may need different treatments. Laser treatment to treat some corneal dystrophies and other conditions, doctors can use a type of laser treatment called phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) to reshape the cornea, remove red tissue, and improve vision.
Since ocular oncology is a very special field of ophthalmology, there is an effective international collaboration between ocular oncologists. Ocular oncology is a versatile service that includes general oncologists, paediatric oncologists, professional nurses, medical scientists, and many more. Severe symptoms including uveal and conjunctivitis melanoma, uveal metastasis, intraocular and conjunctiva lymphoma, and conjunctiva carcinoma. As well as confirmed treatment for malignant tumors, ocular oncologists found a large number of referrals for patients with suspected malignant tissue. Detection is based on biomicroscopy, ultrasonography, angiography, optical coherence tomography, auto fluorescence imaging, and biopsy. The most common malignant tissues include naive, chordal hemangiomas. Many of these lesions need treatment and/or long-term care. The eyelid and orbital tissues may be controlled within the services of oculoplastic or orbital specialists.
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to vision loss. Cataract usually develops slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include dull colours, blurred or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and night vision problems. This can lead to difficulty driving, reading, or facial expressions. Cataract blindness can also lead to falls and depression. Cataract causes about half of all blindness cases and 33% of visible disabilities worldwide.
A Cataract is more common due to aging but may also be due to trauma or radiation exposure, birth defects, or eye surgery. Possible factors include diabetes, long-term use of corticosteroids, smoking, prolonged exposure to the sun and alcohol. A basic inexplicit mechanism involves the accumulation of protein molecules or a yellowish-coloured lens that reduces light transfer to the retina behind the eye. Detected by an eye examination.
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition that can lead to blurred vision or hallucinations during the visual field. During the early stages, there are often no symptoms but over time, some people experience a gradual deterioration of vision that can affect one or both eyes. Although it does not cause complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it difficult to see the face, drive, read, or perform other activities in daily life. Visual hallucinations can be seen but this does not mean any mental illness.
Macular degeneration commonly occurs in older people. Genetic and smoking factors also play a role. It is due to damage to the retinal macula. Diagnosis is a complete eye examination. The difficulty is divided into early, medium, and late types. The latter version was further divided into "dry" and "wet" forms with a dry form making up 90% of cases.
This is a specialty in the prevention, treatment, and curing of paediatric eye diseases and vision health. Good eye care is important during childhood, as these are the years when eye-sight-related problems can arise as the eyes grow and can affect their future growth. Children's eyes are continuously growing until they are 8 years old.
Diseases affecting children's vision include hereditary eye diseases, paediatric uveitis, developmental disorders, and more. There are many genetic diseases that need to be scrutinize in the first place. Amblyopia is a disease that occurs as a result of reduced vision in the eye that has not received adequate use in childhood. Symptoms include tilt of the head, blurred vision, and improper eye movement.
The most common conditions affecting vision during childhood are: congenital diseases ,amblyopia (known as lazy eye) ,strabismus ,inflammation ,infection
Dry eye is a condition in which a person needs additional quality tears to lubricate and support the eye. Tears are important for maintaining a smooth movement of the front surface and for giving a clear impression. Dry eye is a common and chronic problem, especially in more established adults. And a low visual impact that affects the step-by-step performance of a tyke or a low vision as the word indicates a state of being associated with surprising.
Tumors in the eye are usually secondary tissue caused by cancer that has spread from other parts of the body, especially the breast, lungs, intestines, or prostate. Two common types of tissue evolve within the eye itself and are known as retinoblastoma in children and melanoma in adults.
Retinoblastoma is a cancer of the retina, a tissue that is sensitive to light. This common eye cancer in children usually affects children under the age of five, affecting 500 to 600 in the United States each year. In about a third of cases, retinoblastoma appears in both eyes. While symptoms may not be present at the onset of the disease, increasing pain and loss of vision eventually indicate a problem.
Malignant melanoma most commonly occurs in adults aged 60 to 65 years, resulting from uncontrolled growth of cells called melanocytes. From 1,500 to 2,000 new cases are found every year in the United States.
Neuro-Ophthalmology is a specialized unit that focuses on eye-related neurological problems. As we all know, the human eye processes images and transmits them to the brain for processing. It is the optic nerve that transmits these visual aids and the malfunction of this function can cause visual impairment and can lead to irreversible damage.
Cerebral Visual Impairment (CVI) includes all visual defects caused by injury or violation, visual retrieval methods without damage to advanced visual pathways, or any significant visual impairment. Visual problems can be defined as decreased visual acuity. There are a variety of eye problems and vision problems, myopia, halos, blurred vision etc.
Blurred vision problems will reduce visual acuity. It often interferes with a person's daily activities. Myasthenia gravis is caused by malfunction between nerves and muscles that stimulate both visions, hanging eyelids, and different muscle defects that affect both i.e. neuromuscular further vision.
Ophthalmic surgery is also known as ocular surgery is performed on the eye to treat a condition by an ophthalmologist. There are many types of eye surgery including corrective surgery — used to correct or treat ailments. Phacoemulsification is cataract surgery in which the inner lens of the eye is transformed. Glaucoma surgery
is performed to reduce the production of intraocular fluid. Oral surgery is considered mainly for eyelids or orbit and the lacrimal system
Diabetes retinopathy is an eye condition that can cause loss of vision and vision in people with diabetes. It affects the blood vessels in the retina (a layer that is sensitive to light tissue behind your eye). If you have diabetes, it is important that you get a thorough eye examination at least once a year.
Diagnostic & Therapeutic Instruments used in Optometry and Ophthalmology
Diagnostic and therapeutic devices are helpful in diagnosing and treating disease. Eye implants are designed to avoid eye damage, injury. The new optometric practice uses leading-edge techniques, delivers high-quality service, and provides customer satisfaction.
Ophthalmic Genetics and Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is a fast-paced method that controls genetic expression to treat disease. Often, through genetic therapy, genes are implanted in cells to reproduce protein production that may have been impaired due to a patient's DNA. These genes are usually presented with a vector designed to deliver genes to patients' cells. Ophthalmic genetics is a branch of ophthalmology that specializes in the field of research. Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA) is a genetic disorder that causes defects by birth in children. Scientists and doctors have treated the disease with the help of genetic engineering.
Refractive, or optical, errors - myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism - cause blurred vision due to inability to focus on images on the retina. If left unchecked, its effects can be especially dangerous for children, as vision develops in the early years of life.
Strabismus is a condition in which the eyes do not align properly when looking at an object. An eye that is focused on an object can take it in turns . The condition can occur occasionally or frequently. Strabismus can occur due to muscle dysfunction, blurred vision, brain problems, trauma or disease. Risk factors include premature birth, cerebral palsy, and family history of the condition. Types include esotropia, where the eyes are crossed ("cross eyed"); esotropia, in which the eyes divide ("lazy" or "wall-eyed"); and hypertropia when properly differentiated
Uveitis is a form of inflammation of the eyes. It affects the middle layer of tissue in the eye wall (uvea). Warning symptoms of Uveitis (vee-I-tis) usually come suddenly and get worse quickly. It includes redness of the eyes, pain and blurred vision. This condition can affect one or both eyes, and it can affect people of all ages, even children. Possible causes of uveitis infection, injury, or autoimmune or inflammatory disease. Often the cause cannot be identified. Uveitis can be major, leading to lifelong vision loss. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and to maintain a positive outlook.
Optical Imaging is a method by which light is used to obtain an investigative image of medical services. Basically, optical imaging is of two types which are different imaging systems and a ballistic imaging system. Some of the major examples are laser ophthalmoscopy scanning, optical coherence tomography, optical microscopy and endoscopy, spectroscopy.
Eye floats or dots in a person's vision appear to float when a person tries to look at them directly. They are formed by the vitreous of the eye, and in many cases, completely normal. The vitreous is a clear, gel-like substance that fills most of the eye.
Age Related Eye Disease (AREDS)
The Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS) and AREDS2 are major clinical trials sponsored by the National Eye Institute. The AREDS study is designed to learn more about the natural history and risk factors of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and cataract and to assess the effect of vitamins on the progression of these eye diseases There are four types of age-related eye diseases (AREDs) that affect adults: glaucoma, cataract, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy. Learning about the symptoms and treatments for each of these conditions can help you to protect your own and that of an elderly loved ones.
The red-eye (conjunctivitis) is a swelling or infection of the conjunctiva that covers the eyelid and covers the white part of your eye. When the small blood vessels in the conjunctiva become inflamed, they become visible. This is what makes the whites of your eyes look pink or pink.
Symptoms include redness, itching and tearing of the eyes. It can also lead to discharge or riming near the eyes.
It is important to stop wearing contact lenses during conjunctivitis. It usually resolves on its own, but treatment can speed up the recovery process. Allergen conjunctivitis can be treated with antihistamines. Bacterial conjunctivitis can be treated with antibiotic eye drops.
How it spreads by skin contact (shaking or hugging).
Retinal detachment is the most serious condition of the eyes that occurs when your retina - the layer of tissue behind your light-producing eye - is pulled away from the surrounding tissue. Doctors also call it a detached retina.
Since your retina may not function properly when this happens, you may have permanent vision loss if you do not get treatment immediately.
Colour blindness (colour blindness) is a reduced ability to detect colour or colour difference. It can interfere with activities such as picking ripe fruit, choosing clothing and learning about traffic lights. Colour blindness can make some educational activities more difficult.
In most cases, color defects are caused by a genetic defect in the child. This is because some color-sensitive cells in the eyes, called cones, are lost or misaligned.
It is a healthcare profession that is autonomous, educated, and regulated (licensed/registered), and optometrists are the primary healthcare practitioners of the eye and visual system who provide comprehensive eye and vision care, which includes refraction and dispensing, detection/diagnosis and management of disease in the eye, and the rehabilitation of conditions of the visual system.
Market Analysis
Ophthalmic devices market by product function (Surgical devices- Refractive error surgery devices, Glaucoma surgery devices, Cataract surgery devices and Vitreoretinal surgery devices; Ophthalmic diagnostic devices- Refractors, Corneal topography systems, Retinal ultrasound systems, Fundus camera, Ophthalmoscopes, OCT, Perimeters, Slit lamps and Tonometer; and Vision care devices- Contact lenses and spectacles) size was valued at $53,428.8 million in 2019, and is projected tp reach $66,719.3 million by 2027, registering a CAGR of 4.2% from 2020 to 2027.
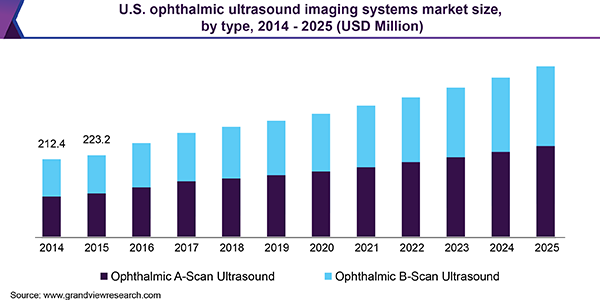

The emergence of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, and the resulting disease Covid-19, has created a major international public health challenge. As the government has imposed lockdown, the ophthalmology diagnostics clinics are closed and the surgeries are postponed which is expected to limit the growth of the market.
Region wise, the ophthalmic devices market is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. The North America ophthalmic devices market accounted for the largest share in 2019; however, Asia-Pacific is anticipated to register the highest CAGR of 4.6% throughout the forecast period. According to the Center for Diseases Control and Prevention, diabetic retinopathy is expected to account for major cause of blindness in the U.S. From 2010 to 2050, the number of Americans with diabetic retinopathy is expected to nearly double from 7.7 million to 14.6 million. Glaucoma further contributes toward the loss of vision and blindness.
Young Scientists Benefit
- Our conferences provide an excellent Platform for your research through oral presentations.
- Share ideas with leading researchers and consultants.
- Young Scientist Award re-certification certificate and a reminder to the winners
- Junior Scientists will receive relevant and up-to-date information on this Forum.
- A collaborative platform among junior investigators for better development
- The award should encourage participants to strive for their full potential which can be beneficial to the whole sector
Target Audience
Ophthalmologists, Optometrists, Opticians, Doctors, Researchers, Students, Industrial Delegates from Academia and Research along with the industrial professionals from biomedical companies and healthcare sectors.
·Clinical researchers & Scientists
.Medical Practitioners, Professors, Deans, Students & Technicians
.Medical & Health care Organizations & Associations
.Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension – Ocular Migraine
Diagnostic Instruments in Optometry
Why to attend
A big reason for attending the conference is to meet with likeminded people and industry peers. This conferences bring together people from all different geographical areas who share a common discipline or field, and they are a great way to meet new people in your field.
To expand your knowledge and find solutions to problems
You will hear a lot about things in your field that will be new to you. These could be new techniques, new types of equipment, unpublished data, or learn from thought-leaders that you may not have previously heard of.
To present your ideas and work to others
This is one of the more obvious reasons for attending conference to present your work. It’s good practice in talking about what you do with a variety of people from similar, related and/or completely different areas of study.
Conference Highlights
- Ophthalmology
- Glaucoma: A Vision Loss
- Cornea Disorders and Treatments
- Ocular Oncology
- Cataract
- Macular Degeneration
- Paediatric Ophthalmology
- Dry Eye & Low Vision
- Eye tumours
- Neuro - Ophthalmology
- Ophthalmology surgery
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Diagnostic & Therapeutic Instruments used in Optometry and Ophthalmology
- Ophthalmic Genetics and Gene Therapy
- Refractive Errors in children
- Strabismus
- Uveitis
- Optical Imaging and Sensing:
- Eye Floaters
- Age Related Eye Disease (AREDS)
- Conjunctivitis
- Retina and Retinal Detachment
- Colour blindness
- Optometry
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | May 04-05, 2022 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Clinical & Experimental Ophthalmology
- Journal of Eye & Cataract Surgery
- International Journal of Ophthalmic Pathology.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by



